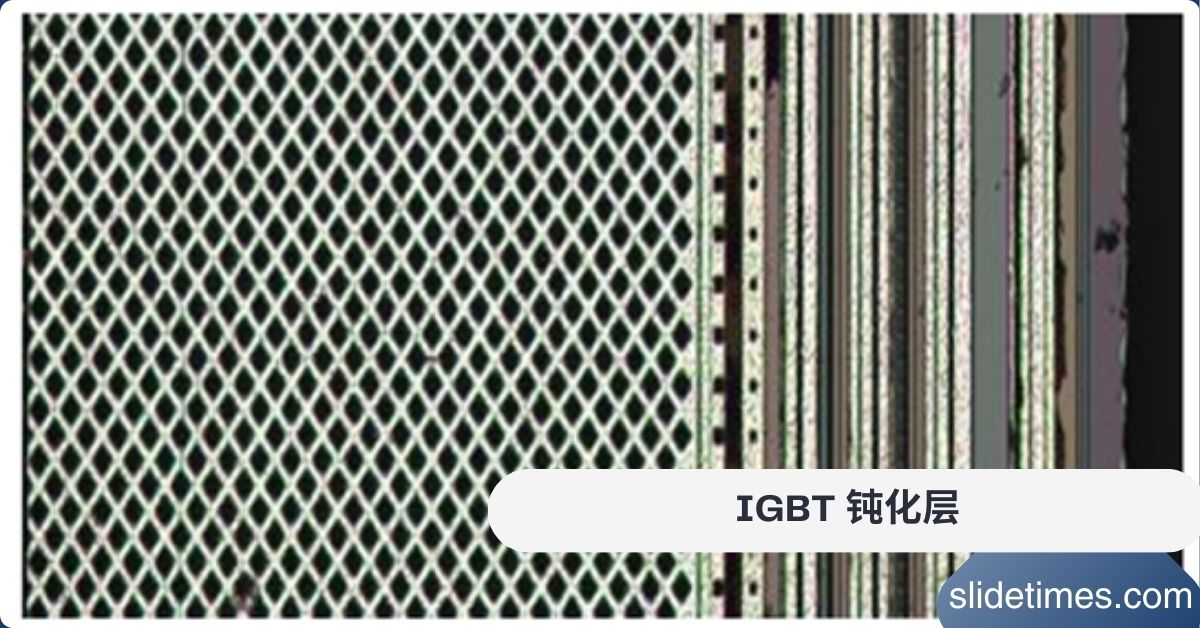
In the world of power electronics, the Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor (IGBT) is a key component that helps control and manage electrical power efficiently. But have you ever wondered what keeps these powerful devices safe and reliable? That’s where the IGBT 钝化层 (passivation layer) comes into play. In this article, we’ll dive deep into what the IGBT 钝化层 is, why it’s important, and how it works. Whether you’re an engineer, a student, or just someone curious about electronics, this guide will break down everything you need to know in simple terms.
What is an IGBT 钝化层?
The IGBT 钝化层 (passivation layer) is a thin protective coating applied to the surface of an IGBT semiconductor. Think of it as a shield that protects the IGBT from external threats like moisture, dust, and chemical contamination. Without this layer, the IGBT could malfunction or even fail, leading to costly repairs or replacements.
The term “钝化层” comes from the Chinese word for “passivation,” which means making something less reactive or inactive. In the context of IGBTs, the passivation layer makes the semiconductor surface less susceptible to environmental damage, ensuring the device operates smoothly for a long time.
The Science Behind Passivation
Passivation is a process that involves creating a non-reactive surface on a material to prevent it from interacting with its environment. In the case of IGBTs, the passivation layer is typically made of materials like silicon dioxide (SiO₂) or silicon nitride (Si₃N₄). These materials are chosen for their excellent insulating properties and ability to adhere well to the semiconductor surface.
The passivation layer is applied using advanced techniques such as chemical vapor deposition (CVD) or physical vapor deposition (PVD). These methods ensure that the layer is uniform and free of defects, which is crucial for its effectiveness.
The Role of the Passivation Layer in IGBTs
The primary role of the passivation layer in IGBTs is to protect the semiconductor surface from environmental factors that could cause damage. This includes moisture, dust, and chemical contaminants, which can lead to corrosion, electrical leakage, and ultimately, device failure.
In addition to protection, the passivation layer also plays a crucial role in stabilizing the electrical properties of the IGBT. By insulating the semiconductor surface, the passivation layer helps maintain consistent performance, even under varying conditions such as temperature fluctuations and humidity.
Also Read: Gmail Gina Villar San Francisco: Everything You Need to Know
Why is the IGBT 钝化层 Important?
The IGBT 钝化层 plays a critical role in the performance and reliability of IGBTs. Here’s why it’s so important:
1. Protection from Contamination
One of the primary functions of the passivation layer is to protect the IGBT from contamination. Dust, moisture, and chemicals can all cause damage to the sensitive semiconductor material. The passivation layer acts as a barrier, keeping these contaminants out and ensuring the IGBT operates smoothly.
2. Preventing Electrical Leakage
Electrical leakage is a common issue in semiconductors, where electrical charges escape from the intended path, leading to inefficiencies and potential failures. The passivation layer insulates the semiconductor surface, reducing the risk of electrical leakage and ensuring the IGBT operates efficiently and safely.
3. Enhancing Durability
By shielding the IGBT from environmental stressors, the passivation layer extends the device’s lifespan. This is particularly important in applications where the IGBT is exposed to harsh conditions, such as high temperatures or humidity. A durable passivation layer can save time and money on replacements and repairs.
4. Improving Performance
A well-applied passivation layer ensures stable operation, even in challenging conditions. This is crucial for maintaining the performance of the IGBT, especially in high-power applications where reliability is key.
How Does the IGBT 钝化层 Work?
The IGBT 钝化层 is typically made of materials like silicon dioxide (SiO₂) or silicon nitride (Si₃N₄). These materials are chosen for their excellent insulating properties and ability to adhere well to the semiconductor surface.
Step-by-Step Breakdown of How the Passivation Layer Works
- Application: The passivation layer is applied to the IGBT surface using techniques like chemical vapor deposition (CVD) or physical vapor deposition (PVD). These methods ensure the layer is uniform and free of defects.
- Insulation: Once applied, the layer acts as an insulator, preventing electrical charges from escaping or entering the semiconductor material.
- Protection: The layer shields the IGBT from environmental factors like moisture, dust, and chemicals, which could otherwise cause corrosion or short circuits.
- Stabilization: By maintaining a stable surface, the passivation layer ensures the IGBT operates consistently, even under varying conditions.
The Importance of Uniformity and Adhesion
For the passivation layer to be effective, it must be applied uniformly and adhere well to the semiconductor surface. Any weak spots or defects in the layer can lead to failures, such as electrical leakage or contamination. Advanced application techniques, such as CVD and PVD, are used to ensure the layer is uniform and defect-free.
Also Read: Can I Get a Photo of Stasha Mikov? Exploring the Artistic Journey of a Rising Star
Materials Used in IGBT 钝化层
The choice of material for the IGBT 钝化层 is crucial for its effectiveness. Here are the most common materials used:
1. Silicon Dioxide (SiO₂)
Silicon dioxide is the most widely used material for passivation layers. It’s highly insulating, easy to apply, and provides excellent protection against moisture and contaminants. SiO₂ is also relatively inexpensive, making it a popular choice for many applications.
2. Silicon Nitride (Si₃N₄)
Silicon nitride is known for its superior mechanical strength and resistance to high temperatures. It’s often used in IGBTs that operate in extreme conditions, such as high-power applications or environments with significant thermal stress.
3. Polyimide
Polyimide is a polymer-based material that is flexible and offers good thermal stability. It’s used in applications where the IGBT may experience mechanical stress, such as in flexible electronics or devices that undergo frequent movement.
4. Aluminum Oxide (Al₂O₃)
Aluminum oxide provides excellent electrical insulation and is often used in high-power IGBTs. It’s also resistant to high temperatures, making it suitable for demanding applications.
Challenges in IGBT 钝化层 Design
While the IGBT 钝化层 is highly effective, designing and applying it comes with its own set of challenges:
1. Uniformity
The passivation layer must be applied uniformly to avoid weak spots that could lead to failures. Any inconsistencies in the layer can result in electrical leakage or contamination, compromising the performance of the IGBT.
2. Adhesion
The layer must adhere well to the semiconductor surface to prevent peeling or cracking. Poor adhesion can lead to defects in the passivation layer, reducing its effectiveness and potentially causing device failure.
3. Thermal Stress
IGBTs often operate at high temperatures, so the passivation layer must withstand thermal expansion and contraction without degrading. Materials with high thermal stability, such as silicon nitride, are often used to address this challenge.
Also Read: Evolvedgross.com: A Comprehensive Guide to the Future of Digital Marketing
4. Cost
High-quality materials and precise application techniques can be expensive, impacting the overall cost of the IGBT. Balancing cost and performance is a key consideration in the design of the passivation layer.
Applications of IGBT 钝化层
The IGBT 钝化层 is used in a wide range of applications, including:
1. Electric Vehicles (EVs)
IGBTs are essential components in EV power systems, and the passivation layer ensures they operate reliably in challenging environments. The layer protects the IGBT from moisture, dust, and temperature fluctuations, ensuring consistent performance.
2. Renewable Energy
In solar inverters and wind turbines, IGBTs with passivation layers help convert and manage power efficiently. The layer protects the IGBT from environmental factors, ensuring reliable operation in outdoor conditions.
3. Industrial Machinery
IGBTs are used in motor drives and power supplies, where the passivation layer protects them from dust and moisture. This is particularly important in industrial environments, where equipment is often exposed to harsh conditions.
4. Consumer Electronics
Devices like air conditioners and refrigerators use IGBTs with passivation layers to ensure long-lasting performance. The layer protects the IGBT from environmental factors, ensuring reliable operation over time.
Future Trends in IGBT 钝化层 Technology
As technology advances, the IGBT 钝化层 is also evolving. Here are some trends to watch:
1. Advanced Materials
Researchers are exploring new materials like graphene and diamond-like carbon (DLC) for even better performance. These materials offer superior electrical insulation and thermal stability, making them ideal for high-power applications.
2. Nanotechnology
Nanoscale passivation layers are being developed to provide superior protection without adding bulk. These layers are thinner and more flexible, making them suitable for advanced electronics and miniaturized devices.
3. Sustainability
Eco-friendly materials and processes are being adopted to reduce the environmental impact of IGBT production. This includes the use of biodegradable materials and energy-efficient manufacturing techniques.
4. Smart Passivation Layers
Future passivation layers may incorporate sensors to monitor the health of the IGBT in real-time. These smart layers could provide early warning of potential issues, allowing for proactive maintenance and reducing the risk of device failure.
Also Read: Fintechzoom.com DAX40: Understanding Germany’s Top 40 Companies
FAQs About IGBT 钝化层
What does “钝化层” mean in English?
“钝化层” translates to “passivation layer” in English. It refers to a protective coating applied to semiconductors to prevent damage and ensure reliable operation.
Why is the IGBT 钝化层 necessary?
The IGBT 钝化层 is necessary to protect the semiconductor from environmental factors like moisture, dust, and chemicals. It also prevents electrical leakage and enhances the device’s durability.
What materials are used for the IGBT 钝化层?
Common materials include silicon dioxide (SiO₂), silicon nitride (Si₃N₄), polyimide, and aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃).
How is the IGBT 钝化层 applied?
The passivation layer is applied using techniques like chemical vapor deposition (CVD) or physical vapor deposition (PVD) to ensure a uniform and defect-free coating.
Can the IGBT 钝化层 fail?
Yes, if the passivation layer is not applied correctly or is damaged, it can lead to device failure. Proper design and application are crucial for its effectiveness.
What are the future trends in IGBT 钝化层 technology?
Future trends include the use of advanced materials like graphene, nanotechnology for thinner layers, and smart passivation layers with built-in sensors.
Conclusion
The IGBT 钝化层 is a small but mighty component that plays a vital role in the performance and reliability of IGBTs. By protecting the semiconductor from environmental damage and ensuring stable operation, it helps power everything from electric vehicles to industrial machinery. As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more innovative developments in passivation layer materials and techniques, making IGBTs more efficient and durable than ever before.
Whether you’re an engineer designing the next generation of power electronics or simply someone curious about how these devices work, understanding the IGBT 钝化层 is key to appreciating the incredible technology that powers our modern world.